

Hurricane Andrew caused $26.5 billion in damage, making it the most expensive and most destructive hurricane on record in American history at the time, according to the NHC. The transformation also required the strengthening of the structures of homes in the event that another "Big One" came ashore, bringing dangerous winds and rain with it.
#Andrew hurricane track series#
It also sparked a series of changes to Florida's building codes - revealing shoddy business practices and poor enforcement of building codes in South Florida. The storm was eventually known colloquially as "The Big One" and displaced hundreds of thousands of residents in Miami-Dade County - their homes reduced to rubble. Others who decided to ride out the storm described hunkering down in small rooms as powerful winds that carried the sounds of a freight train ripped off exterior downs, allowing rain coming down horizontally to enter. MORE: Hurricane Andrew 25 years later: The monster storm that devastated South Miami "People may think they have more time than they do," Shepherd said. Andrew was also one of the costliest hurricanes on record, incurring 27.3 billion in damage in 1992, which would cause 106 billion in damage if the hurricane. This is why it is especially important for people to heed early warnings and take action as hurricane threats approach. "Particularly in this era of climate change, where we know that the intensity of storms is likely amplified because of these warmer ocean waters, we're going to see a generation of rapidly intensifying storms," Shepherd said. While meteorologists have always known the possibility of rapid intensification, there has been an uptick on rapidly intensifying storms over recent years, Marshall Shepherd, director of the Atmospheric Sciences Program at the University of Georgia and former president of the American Meteorological Society, told ABC News. Warmer ocean waters are likely to blame for an apparent increase of rapid intensification behavior, the experts said. NOAA scientists now use an array of satellite information, land-based, sea-based, and aircraft-related instruments to collect observational data. Looking at the storms in recent hurricane seasons, meteorologists have seen systems clocking in at a Category 2 at nightfall that had suddenly intensified to a Category 4 by morning, Shepherd said. NOAA’s National Hurricane Center has drastically improved its track and intensity forecasts, increasing track accuracy by 75 and intensity forecasts by 50 since Hurricane Andrew.
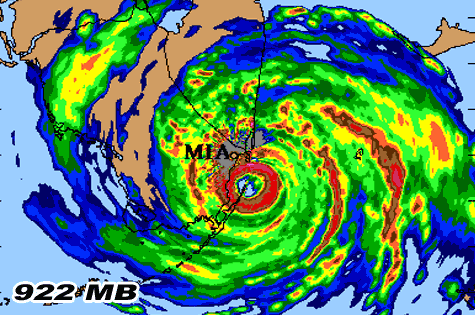
MORE: Updated hurricane outlook still points to above-normal Atlantic season, NOAA saysīlake emphasized that while meteorologists are getting better at predicting how hurricanes will behave, the science is not yet perfect.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
